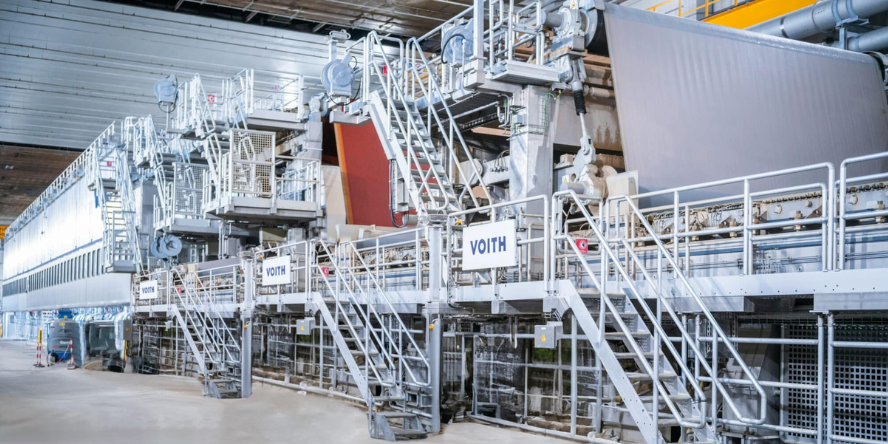
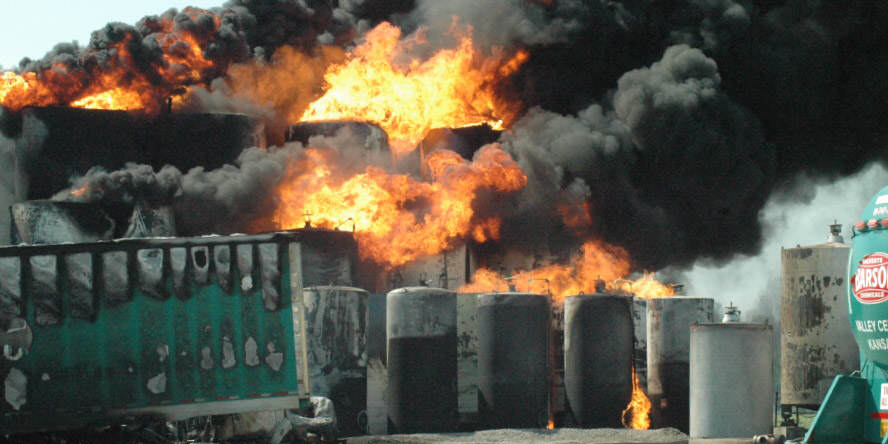
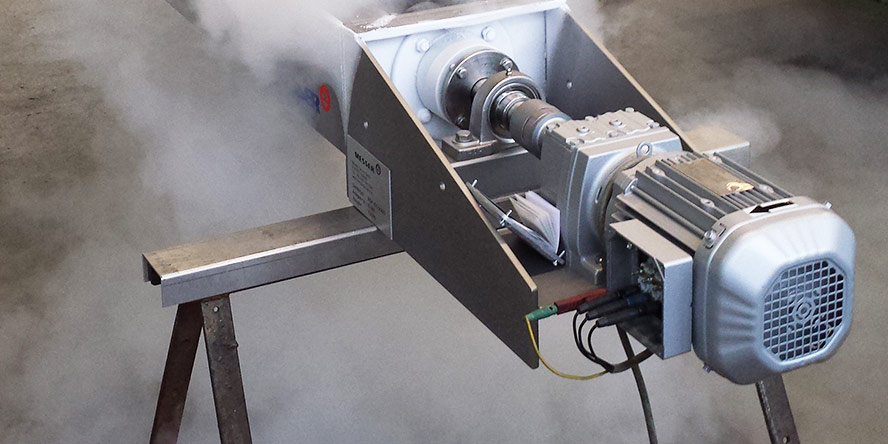
Industrial mist extinguishing systems
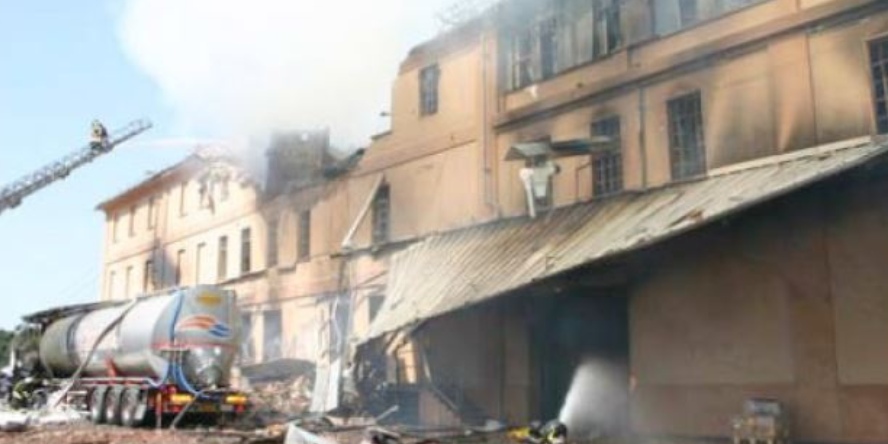
Water mist suppression systems are known for their effectiveness for large surfaces and safety for sensitive equipment. However, mist extinguishing systems for industrial plants must be installed in accordance with the guidelines of VdS, PN-EN, NFPA, or FM GLOBAL, depending on the requirements of your insurer.
VARIETY OF INDUSTRIAL FACILITIES
- power engineering
- wood industry
- food industry
- waste processing
- chemical & petrochemical industry
- other
COMPLIANCE
WITH STRICT REQUIREMENTS
- PN-EN
- VdS
- FM Global
- NFPA
FAMILIARITY WITH DIFFICULT WORKING CONDITIONS
We know the challenges of industrial plants inside-out!
We will match industry-specific components to your working environment
We completed hundreds of industrial projects, including in the corrosive C5M/C5-I environment!
We can meet your insurer’s requirements together!
IIt is the insurance audits and their follow-up requirements for manufacturing companies that often bring clients to us. Regardless of the requirements set by your insurer, we can meet them all.
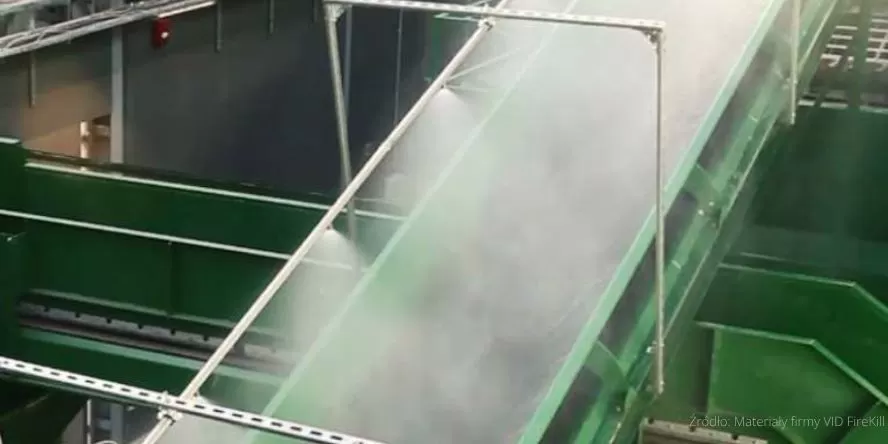
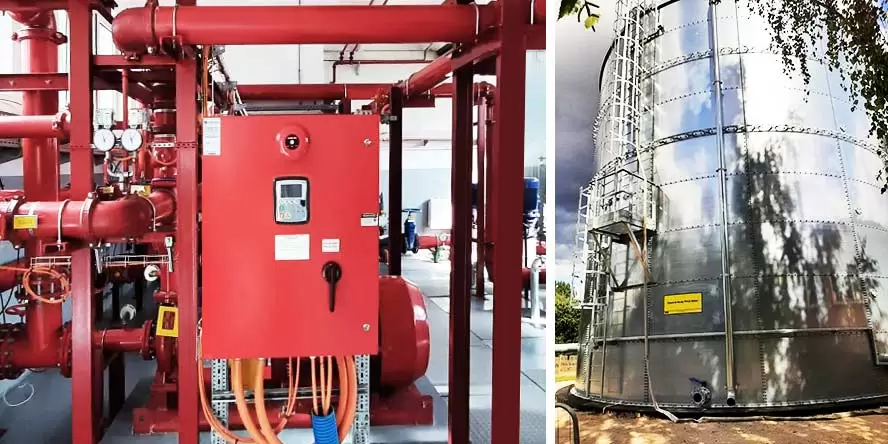
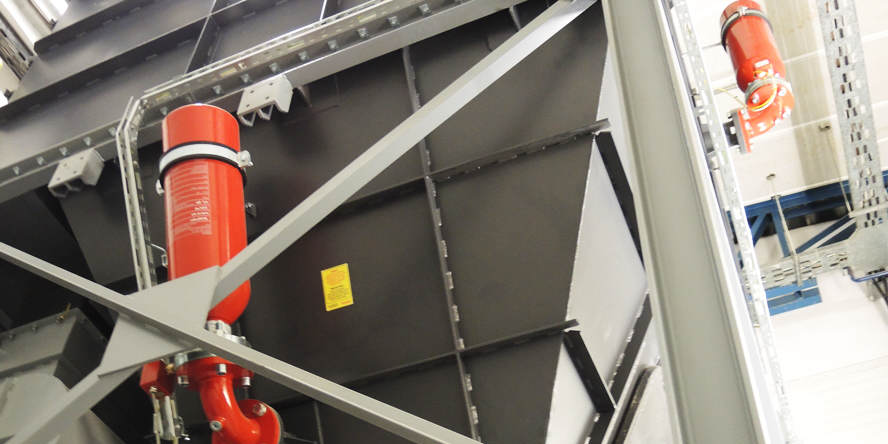
Low-pressure water mist extinguishing system
is best suited to protect:

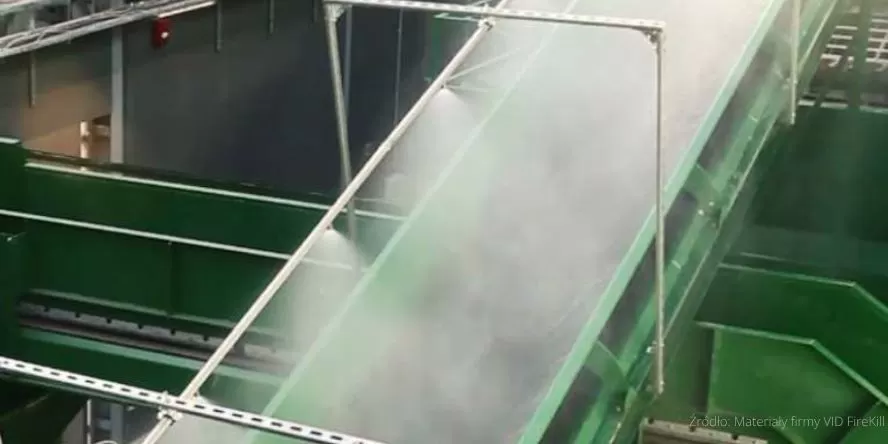
Belt feeders for coal and biomass

Machines and production lines

Lightweight production halls

High-risk production facilities

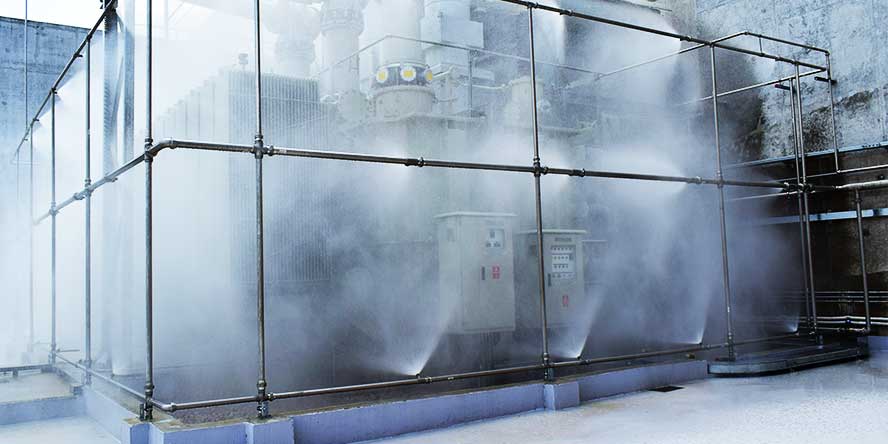
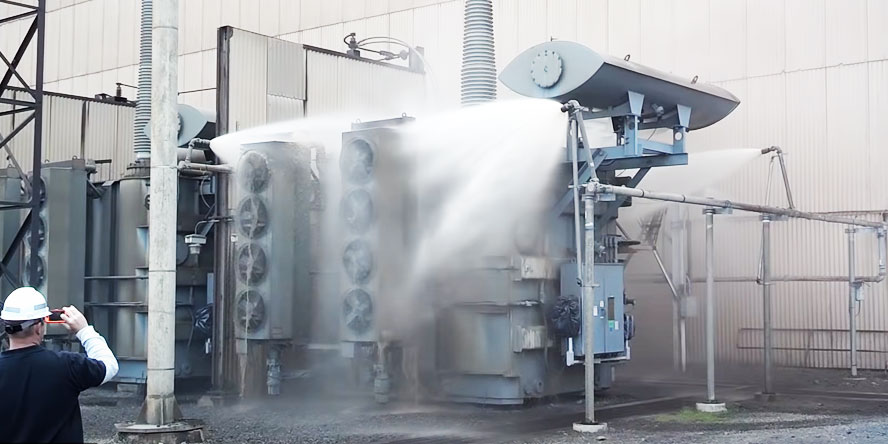
Transformers and oil tanks

Any limited industrial space
Industrial plant vs shopping mall: what’s the difference in fire protection?
Installing a fire protection system (including mist installations) in an industrial facility is quite unlike setting up one in a commercial or office facility. For details, see below:
| THE CHALLENGE | COMMERCIAL FACILITIES | INDUSTRIAL FACILITIES | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk of disruption to the facility's operation during assembly | None, or minimal. Mist systems are most often installed at the construction of the facility, or outside normal operating hours. | Large or high. Assembly is most often carried out during normal operation of the facility Therefore, practical experience in plants is important to minimize this risk. | ||
| Access to scaffolding, trolleys and lifts | Free. Most often the space is free of clutter, and scaffolding, trolleys and lifts can be used without any problems. | Significantly restricted. Tightly packed production halls offer limited access to mist system installation points. | ||
| Risk of collision of the constructed water mist extinguishing system with the infrastructure of the production hall | Zero or minimal. The space is still undeveloped, the assembly team has much freedom of movement. | High. The existing devices and auxiliary installations, often high-rise, hinder assembly works. | ||
| Occupational health and safety regime | The work is carried out in the standard OHS regime. | The work is subject to a high health and safety regime, which requires arrangements and clearance for work. |
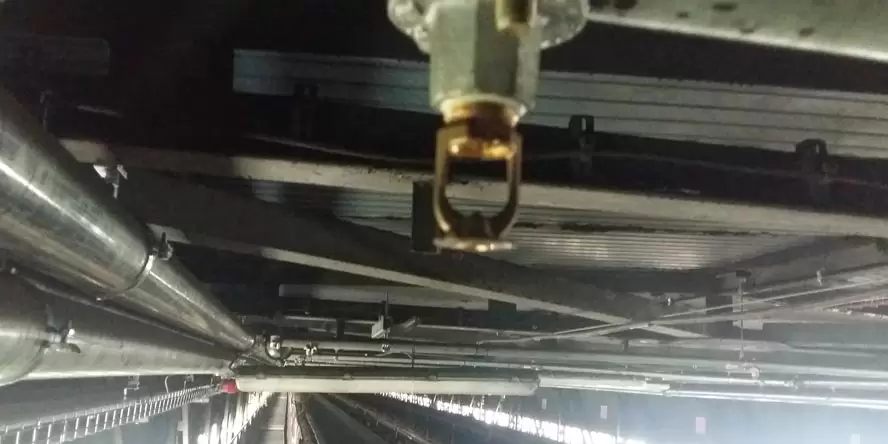
Structure and operation of a water mist system
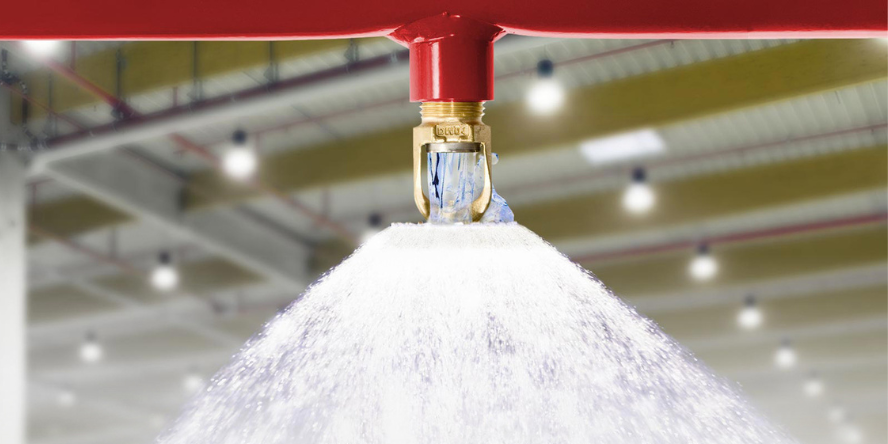
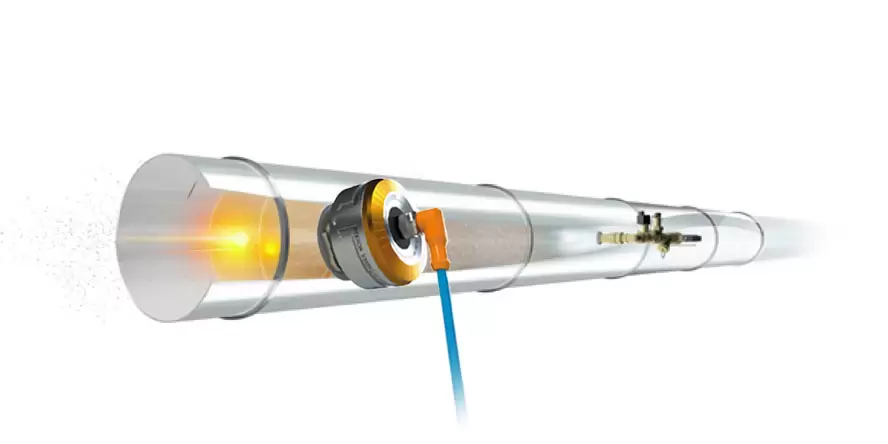
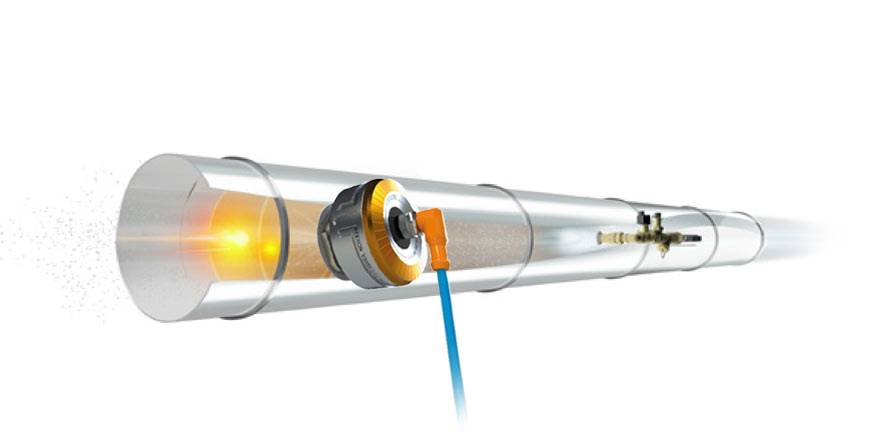
How does mist extinguishing system work?
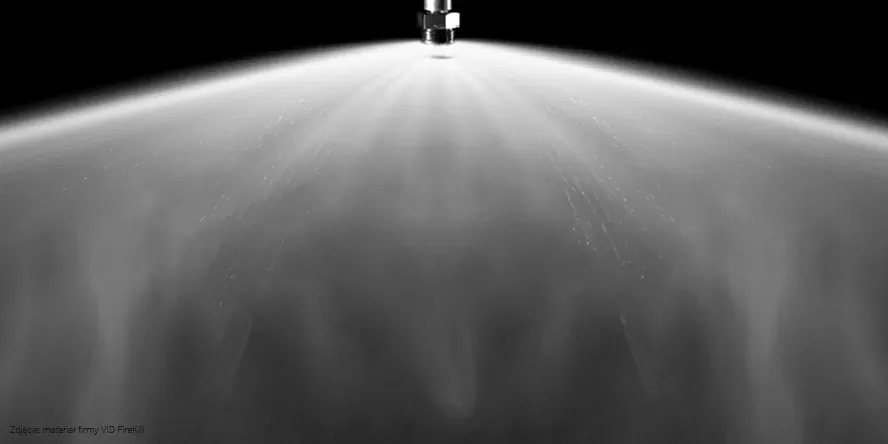
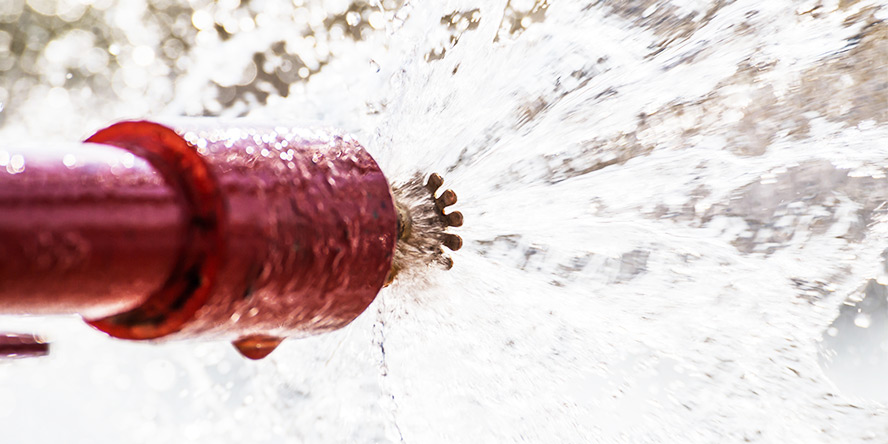
Water mist system is fixed fire extinguishing equipment. It sprays mist, i.e. a huge amount of tiny water droplets (50 – 450 micrometers), under a specified pressure. Water mist allows for faster heat exchange than in the case of regular water installations. The exchange rate depends on the surface area, the temperature difference between the droplets and the surroundings, and the heat transfer coefficient. The latter is determined taking into account the material parameters, as well as the diameter and speed of water droplets.

Water mist system: well-proven components
When designing and installing water mist systems, we only use quality solutions certified by an accredited laboratory. The certification must come with a positive full-scale fire extinguishing test. We need to make sure that the water mist system uses much less water than the sprinkler and deluge installation will be able to easily suppress a fire in your plant. In the case of non-standard facilities, or when a water mist system is used, we can perform additional tests to confirm the effectiveness of the fire system, for absolute certainty.

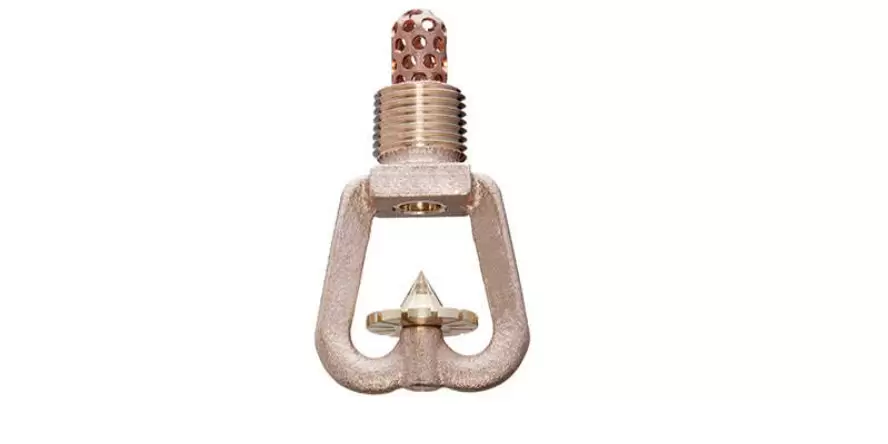
Water mist system: how to select nozzle components?
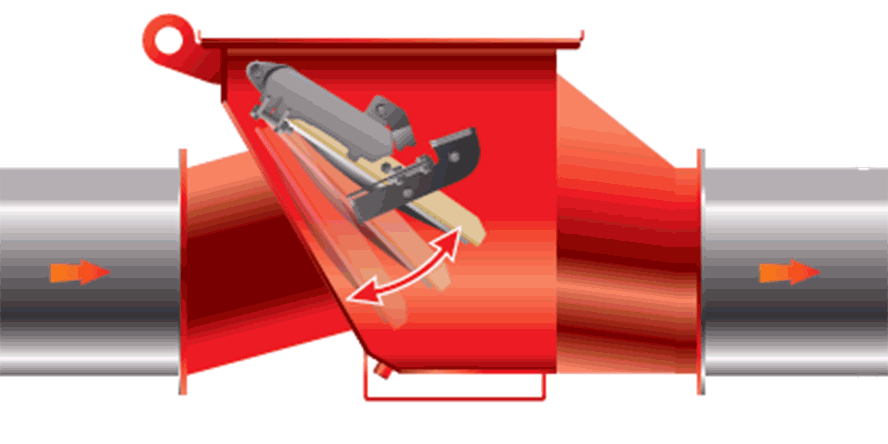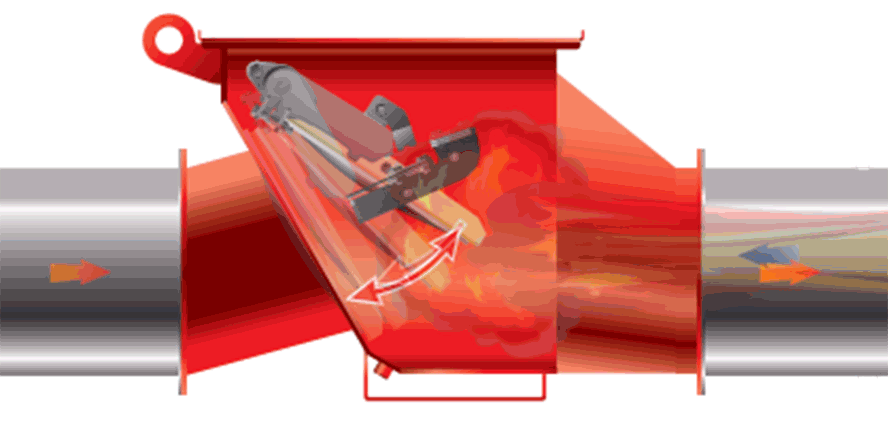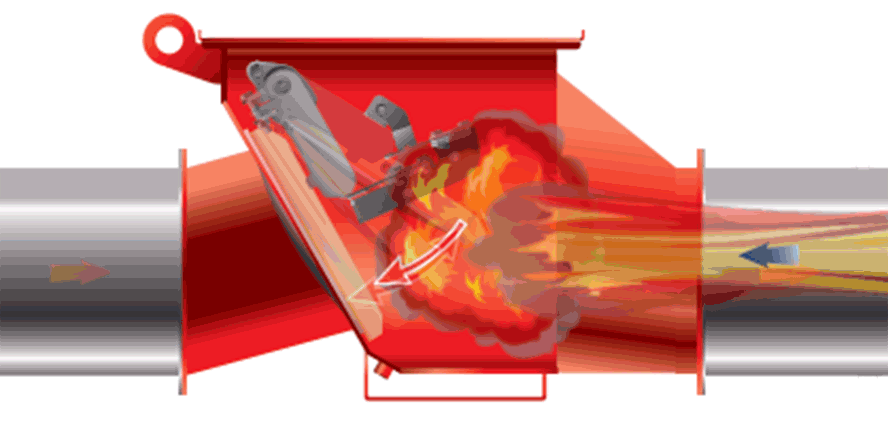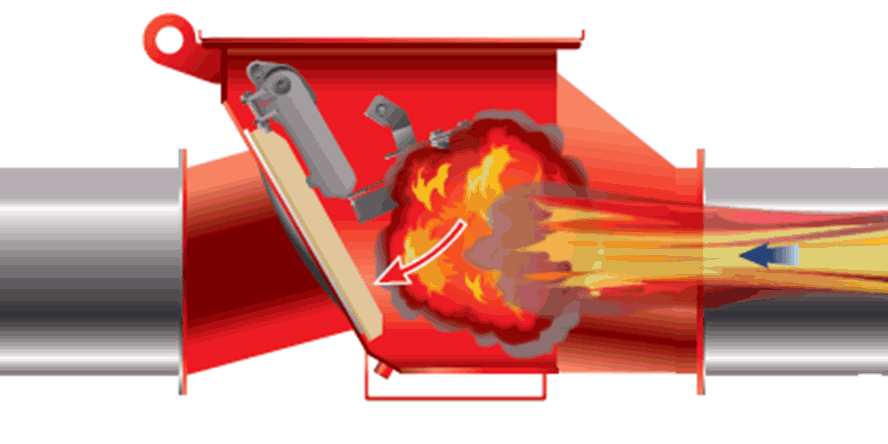
The water mist system allows for the use of both nozzles with a thermosensitive element (as in sprinkler installations), as well as of open nozzles (as in deluge systems).
In the case of a closed system, the nozzle can also be permanently filled with water, as in sprinkler systems. It can also be dry, i.e. filled with pressurized air, the outlet of which activates the water supply. Therefore, the selection of appropriate components of the mist installation (e.g. the type of valves, pumps used, or the need for a detection system) is directly related to the type of nozzles selected to protect a specific area or room.
Cooling or extinguishing with water mist?
Mist extinguishing systems can be designed and installed not only to put out a fire, but also (or solely) to perform other protective functions. What are the differences in foam installations for extinguishing and for cooling?
EXTINGUISHING

Research shows that in large volumes, water mist with larger droplets is more effective than that with smaller droplets.
Oxygen displacement is less important when the goal is to extinguish a fire than when cooling fuel or misting the surroundings.
COOLING

Cooling requires slightly larger droplets so that when they come into contact with the object they cannot evaporate too early.
If mist is used to cool the environment, the droplets should be smaller. It is best to choose nozzles that provide an appropriate mix of droplets, e.g. 150-300 micrometers.
Hassle-free assembling of the mist system
We understand that production processes such as manufacturing, packaging, or storage are key to production profit. That is why we assemble mist systems in such a way as to minimize disruption to the production process.
Based on experience, we anticipate potential challenges already in the design phase, and solve them. We know how to cooperate effectively with production managers to coordinate the assembly process. Our installation operations are scheduled only for specific days and times. We adapt to planned production downtime or periods of reduced work intensity. When necessary, we work at night. We always adapt our work methods to the character of the production plant.
We eliminate production downtime, or bring it down to a minimum
We coordinate assembly with the production schedule
We organize the necessary equipment, e.g. aerial lifts/scaffolding/climbers
We adhere to all internal procedures of the plant
If necessary, we also work at night and on weekends
We only move and work within clearance zones
Before assembly, we secure machines and devices
After installation, we clean up and make sure regular production is quickly restored
Ensuring property safety
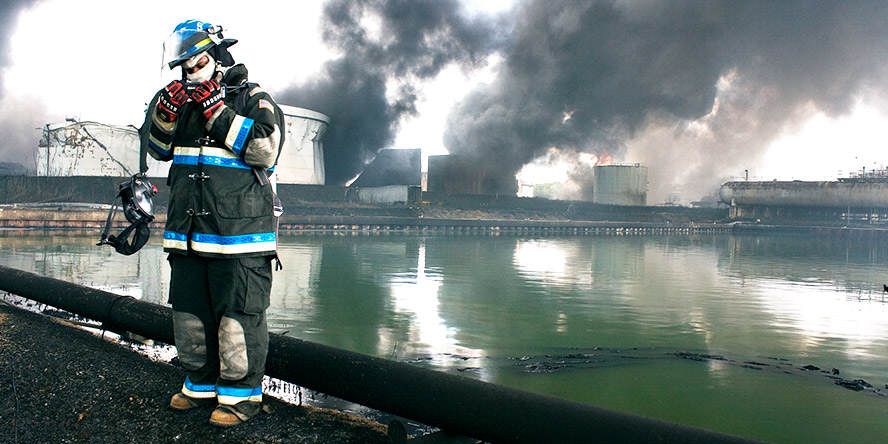
At every stage of our operations, the safety of your assets in halls, warehouses and other production spaces, is crucial for us. We are aware that any damage we cause can have repercussions for the continuity of production and take caution to prevent such situations.
BEFORE THE ASSEMBLY

We agree on the scope of work with the investor
We familiarize ourselves with the safety guidelines
We secure the workplace
We cover machines and devices
DURING AND AFTER ASSEMBLY

We move about with utmost caution
We secure property from damage
We clean the site thoroughly afterwards
We enable production to be restored immediately
- developing the concept and necessary blueprints
- selecting and delivering key installation elements
- developing and implementing a control system
- visualizing the water mist system
- integration of the system with existing security systems
The water mist extinguishing system is a special type of application of water as an extinguishing agent. Due to the fact that during water mist extinguishing we are dealing with very fine water droplets, the physical phenomena occurring during the extinguishing process are slightly different from those we can observe during water extinguishing in classical systems.
The best extinguishing effect can be achieved by individually selecting the size of the droplets according to the purpose of the application, the type of fire and the space covered. This makes it possible, so to speak, to control the physical phenomena we want to achieve during a fire emergency. Thus, for example, the fog may not reach the flames or burning material directly, as it may evaporate already when approaching the fire source.
Accordingly::
- water mist begins to displace oxygen from the immediate vicinity of the flames faster than with water, since it will evaporate much more quickly (applies to enclosed spaces or operation in a large firefighting zone).
- Since water mist evaporates faster, it takes up heat from the burning material much more effectively than when using classical water systems (sprinklers/sprinklers). It lowers the temperature, ambient, flames and fuel, which reduces the amount of heat energy that contributes to the development of pyrolysis and oxidation of the fuel. Thus, it can be said that water mist has the strongest effect on energy in the combustion triangle
- mist under certain conditions also has the ability to affect the concentration of oxygen
- with larger droplets, it also affects the fuel arm in the combustion triangle, producing a layer of water similar to sprinklers. By affecting more than one arm of the triangle, less extinguishing agent can be used to achieve the effect.
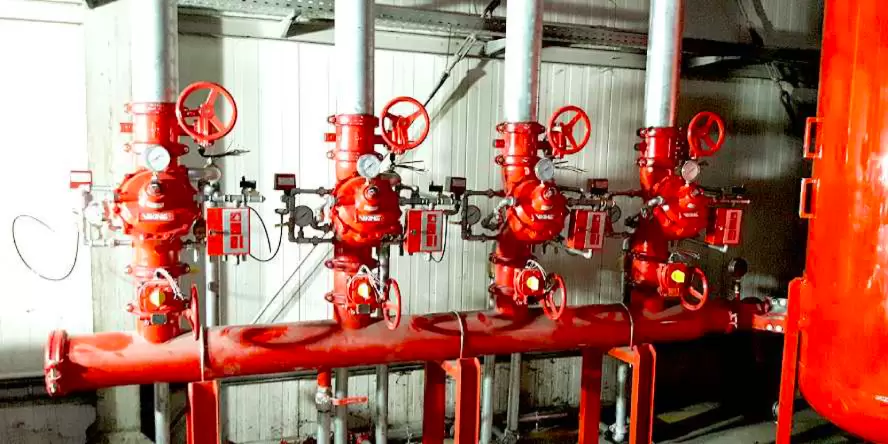
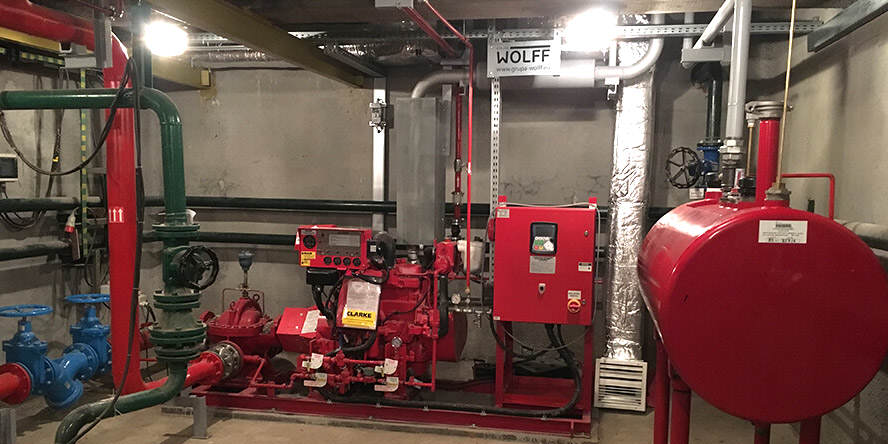
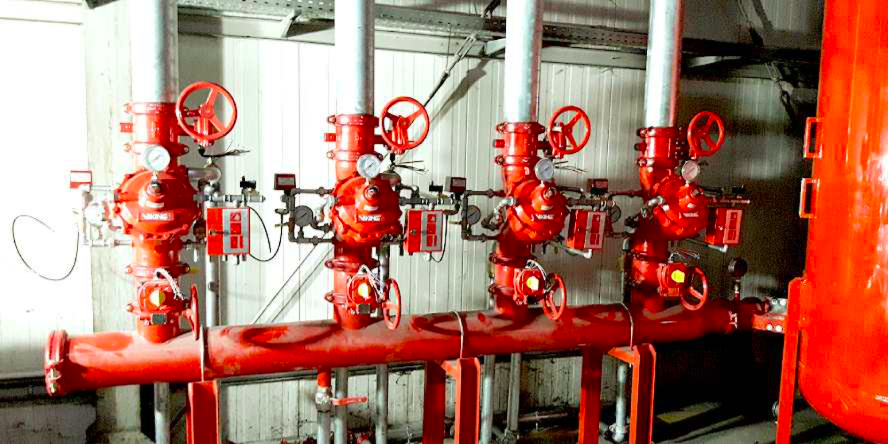
Water mist extinguishing systems can achieve the required spray pressure by supplying from ordinary fire water tanks and appropriately selected pumps, or also by using one or more tanks filled with pressurized water.
Pumps are a practical solution to ensure constant high water mist pressure during firefighting operations. In the case of smaller areas, and thus less demand for water, you can consider forgoing the construction of pumping stations in favor of tanks filled with pressurized water. The cost of such an investment is likely to be lower, however, it should be taken into account that such a water source is usually dedicated to a single firefighting zone. More firefighting zones in one facility may cause the economic effect to shift towards a pumping system.
Water mist technology is used in such industries as commercial power generation (power plants and combined heat and power plants) including transformer stations, and in the petrochemical industry, among others. In addition to specific industries, these are also fire extinguishing systems that can be used more widely in the protection of cable tunnels, control rooms, production lines, warehouses, or machine rooms.
- In situations where the effectiveness of the water mist system is not sufficiently proven – for example, tests of the effectiveness of the nozzles in an accredited laboratory will not come out positive
- In situations when other solutions are cheaper and equally effective, and the main criterion for purchase is price, and not, for example, the need to use the least amount of water for extinguishing, through fear of destroying the machinery park, long production downtime after extinguishing with ordinary water, etc.